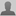UNL archaeological team unearths giant Roman mosaic in southern Turkey
Released on 09/18/2012, at 12:00 AM
Office of University Communications
University of Nebraska–Lincoln







A University of Nebraska-Lincoln archaeological team has uncovered a massive Roman mosaic in southern Turkey – a meticulously crafted, 1,600-square-foot work of decorative handiwork built during the region’s imperial zenith.
It’s believed to be the largest mosaic of its type in the region and demonstrates the reach and cultural influence of the Roman Empire in the area in the third and fourth centuries A.D., said Michael Hoff, Hixson-Lied professor of art history at UNL and the director of the excavation.
“Its large size signals, in no small part, that the outward signs of the empire were very strong in this far-flung area,” Hoff said. “We were surprised to have found a mosaic of such size and of such caliber in this region – it’s an area that had usually been off the radar screens of most ancient historians and archeologists, and suddenly this mosaic comes into view and causes us to change our focus about what we think (the region) was like in antiquity.”
Since 2005, Hoff’s team has been excavating the remains of the ancient city of Antiochia ad Cragum on the southern Turkish coast. Antiochus of Commagene, a client-king of Rome, founded the city in the middle of the first century.
“This region is not well understood in terms of history and archaeology,” Hoff said. “It’s not a place in which archaeologists have spent a lot of time, so everything we find adds more evidence to our understanding of this area of the Roman Empire.
“We’re beginning to understand now that it was more Romanized, more in line with the rest of the Roman world than was suspected before. (The nature of the mosaic) hammers home how Roman this city truly is.”
Antiochia ad Cragum had many of the trappings expected of a Roman provincial city – temples, baths, markets and colonnaded streets, said Hoff. The city thrived during the empire from an economy focused on agricultural products, especially wine and lumber.
Excavation has focused on a third-century imperial temple, and also a street lined with shops. In July, the team began to explore the mosaic, which was part of a Roman bath. The decoration consists of large squares, each filled with different colored geometric designs and ornamentation.
“This would have been a very formal associated pavement attached to the bath,” Hoff said. “This is a gorgeous mosaic, and its size is unprecedented” – so large, in fact, that work crews have uncovered only an estimated 40 percent of its total area.
Hoff said it appears the mosaic served as a forecourt for the adjacent large bath, and that at least on one side, evidence shows there was a roof covering the geometric squares that would have been supported by piers. Those piers’ remains are preserved, he said.
Meanwhile, the middle of the mosaic was outfitted with a marble-lined, 25-foot-long pool, which would have been uncovered and open to the sun. The other half of the mosaic adjacent to the bath is expected to contain similar decoration, Hoff said. Crews expect to unearth the entire work next summer.
Team members first noticed the mosaic in 2001 when a large archaeological survey project that included Hoff noticed a local farmer had plowed up pieces of a mosaic in a field next to a still-standing bath structure. The find was brought to the attention of the archeological museum in Alanya, which two years later made a minor investigation that revealed a small portion of the mosaic.
Last year, the museum invited Hoff to clear the mosaic and to preserve it for tourists and scholars. Hoff’s 60-person team also included Birol Can, assistant professor of archaeology at Atatürk University in Ezrurum, Turkey, a sister university to the University of Nebraska; students from UNL; other students from Turkey and the United States; and workers from a nearby village. About 35 students participated in the project as part of a summer field school Hoff runs.
Phalin Strong, a sophomore art major from Lincoln, said the work was difficult but satisfying.
“It is strange to realize that you are the first person to see this for centuries – a feeling that also made me think about impermanence and what importance my actions have on humanity and history,” Strong said.
Ben Kreimer, a senior journalism major, agreed: “(Working on) the mosaic was great because the more soil you removed, the more mosaic there was,” he said. “Visually, it was also stunning, especially once it got cleaned off. It wasn’t very deep under the surface of the soil, either, so … we had to be careful not to swing the handpick too hard so as not to damage the priceless mosaic that lay just inches beneath us.”
Hoff said the significance of this summer’s discovery has him eager to return to the site and see what the rest of the excavation uncovers.
“As an archaeologist, I am always excited to make new discoveries. The fact that this discovery is so large and also not completely uncovered makes it doubly exciting,” he said. “I am already looking forward to next year, though I just returned from Turkey.”
- Kathe Andersen and Steve Smith
News Release Contacts:
- mhoff1, Professor, School of Art, Art History & Design
phone: 4024725342
Associated Media Files:
- Video interview
- YouTube video
- An overhead perspective of the roughly 40 percent of the mosaic uncovered so far. Researchers expect its total area to be about 1,600 square feet when fully unearthed next summer.
- The mosaic is near a third-century imperial temple in the city of Antoichia ad Cragum, near the Mediterranean on the southern Turkish coast.
- The geometric patterns and ornamentations are quintessentially Roman in design, said Michael Hoff, Hixson-Lied Professor at UNL and the director of the excavation.
- A view of the mosaic uncovered thus far, along with what appears to be a 25-foot-long Roman bath.
- Researchers, students and workers spent two months unearthing and cleaning the mosaic this summer.
- The Roman bath uncovered during the summer.
- A detailed photograph of the tesserae, or tiles, that make up the massive Roman mosaic.