By MTEP 2.0 Outreach Hub members Mohammed Qazi, Tuskegee University; Marilyn Strutchens, Auburn University; and W. Gary Martin, Auburn University
Combining a high-quality secondary mathematics teacher preparation program with attractive qualities like efficiency, affordability, and a generous stipend should normally check off a lot of important boxes for any aspiring teacher. However, as the Developing, Recruiting, and Empowering Alabama Mathematics Teachers (DREAM-Math) Program has experienced, finding candidates can still prove challenging even if the recruitment efforts are conducted on a statewide scale.
DREAM-Math is a Master’s program at Auburn University that prepares teacher candidates to earn initial certification in secondary mathematics education. This initiative, spearheaded by Auburn University, is a Robert Noyce Teacher Scholarship program of the National Science Foundation (NSF) in partnership with Alabama State University and Tuskegee University. It is designed to attract science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) professionals with mathematics-intensive backgrounds to transition to careers in teaching, thereby providing a larger pool of available talent to mitigate the current shortages of secondary mathematics teachers in the United States. To attract these professionals, DREAM-Math offers extensive support through many appealing features, aimed at gaining readiness for the teaching profession, including:
- Affordability, represented by a full-ride Master’s program (in-state tuition and living expenses)
- Efficiency, characterized by a lightning-fast program completion in just four semesters
- High quality, exemplified by a program that provides both the mathematics content knowledge and the pedagogical strategies to teach this content in the classroom, while adhering to best practices aligned with standards
As is the case with many initiatives that have a recruitment aspect, DREAM-Math launched its search for candidates through a flyer and program website. DREAM-Math partner institutions widely disseminated these materials to thousands of eligible alumni and graduating seniors via conventional postings and a comprehensive social media campaign; however, multiple attempts at these efforts resulted in only a small number of inquiries and very few applicants. The project team realized early on that a much wider net would have to be cast to meet the project’s recruitment objectives.
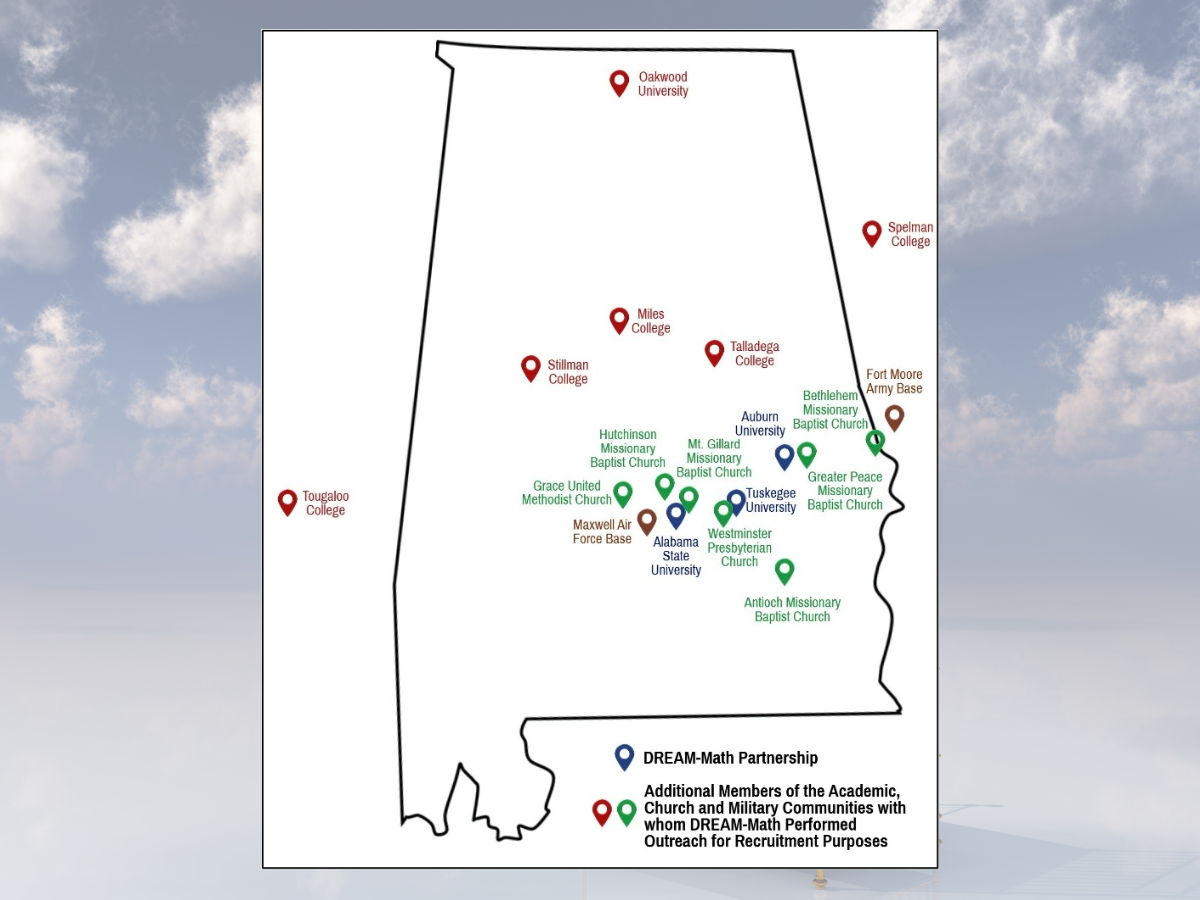
This realization provided the DREAM-Math team with the opportunity to explore unconventional yet deeper-reaching grassroots interventions by intentionally engaging with various communities around the state of Alabama and beyond to discover potential candidates. For example, the team extended recruitment efforts to encompass tutoring centers where tutors may be inclined to transition towards more stable and fulfilling teaching careers. Additionally, they conducted extensive outreach efforts to all Alabama Historically Black Colleges and Universities (HBCUs), as well as some in neighboring states, to identify eligible students from their campuses who might be interested in mathematics teaching careers. Specifically, DREAM-Math personnel successfully used established connections with these HBCUs that they cultivated through previous initiatives. In this context, the main challenge for the project was to reach the appropriate departments and individuals at these HBCUs who could share initial program information with their students.
As another grassroots strategy, the DREAM-Math team forged connections with US military installations in Alabama and Georgia to promote the program among their personnel. In its first two years, DREAM-Math attempted, albeit unsuccessfully, to create links with these military installations. However, a chance meeting with a faculty member at Tuskegee University who also serves as an officer at an Alabama Air Force base finally gave the program the momentum it needed to establish connections with the military. In particular, this officer facilitated communications between the DREAM-Math program and his base’s Publications and Forms Manager and Transition Assistance Manager. The managers used their dissemination network to share about DREAM-Math, which in turn increased awareness of the program at that base and amongst other military units in the state.
For a deeper grassroots approach, the DREAM-Math partnership engaged the clergy in East Central Alabama, enabling DREAM-Math leaders to share about the program during Sunday services in several churches in the region. Interestingly, the idea to engage clergy originated from an informal discussion with a student advisor at Tuskegee, who happened to share about his dual role as the Assistant Chaplain of Tuskegee University. This dialogue ultimately acted as a profound catalyst for DREAM-Math leaders to introduce the program to Sunday congregations, leveraging the Assistant Chaplain’s extensive relationships with clergy across the state. Finally, to offer more comprehensive information regarding DREAM-Math, its leaders organized a monthly evening virtual information session aimed at informing individuals interested in learning more about the program, such as those who may have come across it through our afore-described (and other) interest-generating actions.
Although significantly more time intensive than conventional recruitment methods, the community-based recruitment strategies proved effective in spreading the word about the DREAM-Math program on a large scale. Personal engagement and its multiplicative effects resulted in an increase in inquiries and actual applicants. Interestingly, with all the modern technology at our disposal, the informal word-of-mouth and serendipitous events like the chance encounter with the US Air Force base officer or the casual conversation with the Tuskegee student advisor (the Assistant Chaplain) were successful in promoting the DREAM-Math opportunity.
In conclusion, to maximize the chances of success, any teacher preparation initiative that includes a recruitment element should be nimble and bold enough to push the recruitment boundaries to go beyond the conventional approaches to attract candidates, akin to the grassroots strategies employed by the DREAM-Math partnership.
Auburn University, Alabama State University and Tuskegee University are members of the Central Alabama Mathematics Teacher Education Partnership (CAMTEP).
Acknowledgement: The work described in this article was funded by grants from the National Science Foundation (DUE-2141730, 2141737, and 151040). Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Science Foundation.